The Semi-Aquatic Hunter of the Triassic
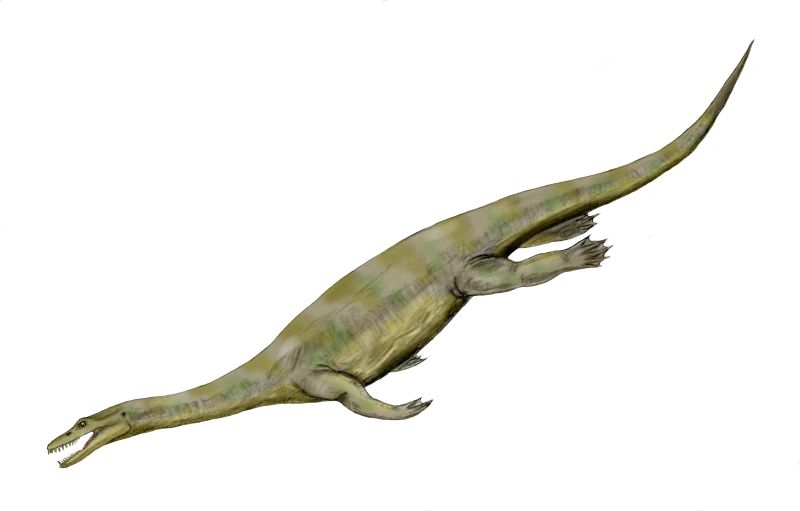
Meet Nothosaurus, a sleek and agile reptile from the Middle Triassic period, around 240 to 210 million years ago!

| Meaning | False lizard [Noth-osaurus] |
| Pronunciation | NO-tho-sore-us |
| When: | Middle Triassic (about 240–210 million years ago) |
| Where: | Europe, Asia (Germany, Switzerland, China) |
| What: | Nothosaur (Nothosaur) |
| Weight: | Estimated around 100–150 kg (220–330 pounds) |
| Length: | Approximately 3–4 meters (10–13 feet) |
| Diet: | Carnivorous (ate fish and other marine animals) |
| Discovered: | First described by Georg Friedrich von Meyer in 1834 |
Nothosaurus was a semi-aquatic reptile, meaning it spent time both on land and in water.
It had a long, slender body, webbed feet, and sharp, needle-like teeth perfect for catching fish.
Nothosaurus likely hunted in shallow coastal waters, using its powerful limbs to swim gracefully through the water and its sharp teeth to snatch slippery prey.
Its elongated snout and streamlined body helped it move quickly, making it an effective predator.
Imagine Nothosaurus gliding through ancient seas, darting after fish and other small marine animals.